Typical organelles Plant cells are cell walls and plastids. The cell wall functions for protection and plastide (chlorophyll) functions for photosynthesis . The following is a complete discussion. This biological article will explain plant cells, plant cell structures, plant cell organelles, the function of their organelles , and plant cell components.
Plant Cells
Cells are the smallest unit of life. Every living thing is composed of many cells ( multicellular ), but some are only composed of one cell ( unicellular ). Plants include multicellular living things. Plant cells are also included in eukaryotic organisms, not prokaryotic. Eukaryotic organisms have a true nucleus that is bound to the membrane (nucleus membrane). Eu means true and karyon means core. The cell size is relatively large (10-100 μm) and has membrane-bound organelles such as RE, golgi bodies, mitochondria, and lysosomes. Eukaryotic cells also have membrane-bound organelles such as ribosomes, microtubules, centrioles and cytoskeletons.Examples of eukaryotic organisms are animals and plants
Other with prokaryotic organisms ...
Prokaryotic organisms are living things whose cell nucleus has no membranes or membranes. Pro means primitive and karyon means core. The size is small (0.5 - 1 μm) and has no organelles with an endomembrane system (nucleus, mitochondria, plastids). Examples of prokaryotic organisms are in the kingdom monera (bacteria and blue algae).
Besides being included in eukaryotic organisms, plants also include autototrophic organisms.
Autotrophs are organisms that are able to convert inorganic substances into organic substances. We often call it an organism that is able to make its own food.
Plants include autotrophic organisms because they have chlorophyll which functions to carry out photosynthesis. Chlorophyll is a leaf green substance produced by chloroplasts organelles.
Besides chloroplasts, plant cells also have other organelles. There are organelles that are only found in plant cells and some are found in other cells.
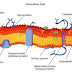
Typical Structure of Plant Cells
Plant cells are typical structures that distinguish them from other cells, especially animal cells. Anyway, we've discussed the differences in animal cells and plant cells in previous biology articles.Read: Differences in animal cells and plant cells
The typical structure of plant cells is as follows:
- The vacuole, in fact other cells also have vacuoles, but are very rare and even if there is a very small size.
- Plastids, one type of plastid that you know is chloroplasts. In addition to chloroplasts, there are also other types of plastide that will be below below.
- Cell wall, this is the structure that makes the body of the plant stiff.
Plant cell organelles and their function
Here are the organelles in plant cells and their functions:1. Nucleus (Core Cell)
The nucleus is the core organelle of a cell. This organelle consists of four parts, namely the Core membrane (Karioteka), nucleoplasm (Kariolimfa), chromatin or chromosome (genetic material) and nucleoli (core child). The function of the cell nucleus is to regulate all cell activity because it contains genetic material (DNA and RNA) which functions to print proteins. Of course you know that protein functions as our body's builders.2. Endoplasmic reticulum (RE)
The endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle consisting of two layers of membrane, cysterna and tube. If we look at the cell image, this RE is like a sheet attached to the cell nucleus.
The RE function is as follows:
- Intracellular transport of material to be secreted
- The means of transporting substances in the cell itself
- Involved in the formation of vacuoles
- Form a membrane in the golgi body
3. Ribosome
Ribosomes are round organelles, very small in size compared to other organelles. Ribosome structure consists of two parts, namely large and small parts. The large part is called a large subunit and the small part is called the small subunit . Ribosomes are composed of proteins and RNA, some are attached along the RE and some are solitary or freely dispersed inside the cell. The function of ribosomes is as a place for protein synthesis4. Mitochondria
The mitochondrial structure is oval, has two layers of membrane (double membrane), the inner layer is curved and is called Krista. Inside the mitochondria there is also DNA.The function of mitochondria is as a cellular respiration center that produces a lot of ATP (energy).
5. Golgi Body (Diktiosom)
The Golgi body or Golgi apparatus consists of a group of cysterna that is flattened and arranged in parallel. The function of the Golgi body is related to the function of cell excretion.6. Plastida
Plastids are divided into three types, namely:- Leukoplas, which is a white plastide that serves as a food store. Leukoplas consists of:
- Amiloplas (to save starch)
- Elaioplas (Lipidoplas) (for storing fat / oil)
- Proteoplas (to store protein)
- Chloroplasts, which are green plastids. This plastide functions to produce chlorophyll and as a place for photosynthesis to take place
- Kromoplas, which is a plastide containing pigments. Kromoplas consists of:
- Carotene (yellow)
- Phikodanin (blue)
- Fikosantin (yellow)
- Phytoerythrin (red)
7. vacuole
The vacuole is a sac surrounded by a membrane that contains fluid / water. Membrane or membrane dividing between vacuoles and cytoplasm is called tonoplas.The function of vacuoles is as follows:
- Water storage, food reserves, oils, enzymes, pigments, toxic compounds and metabolic byproducts.
- Helps maintain turgor pressure in cells.
- Vacuole has an important role as a reservoir for secondary products in the form of liquid, so it is also called 'cell fluid'.
- Some experts say that vacuoles are not organelles (but are nonprotlasmic components).
- In young / meristematic cells, vacuoles are usually small and large.
- Whereas in adult vacuole cells are large.
- Plants do not have an excretory system like animals, therefore vacuoles function to store metabolic waste.
- The place for the destruction of certain compounds by hydrolysis enzymes.
- The vacuole with the vesicles contributes to the storage of material in the cell (the size of the vacuole is greater than the vesicle).
8. Peroxisomes
Is a special organelle equipped with a single membrane. These organelles produce oxidative enzymes that are used in the breakdown of metabolism.
The function of peroxisomes is to help the chloroplast when conducting photorespiration and as a breaker with fat into sugar.
Contains an enzyme that transfers hydrogen from various substrates to oxygen, which produces hydrogen peroxide as a by-product.
Plant cell components
Plant cell components consist of 2 main parts, namely the cell wall and protoplasts.The cell wall is divided into three parts, namely the primary wall, secondary wall and middle lamela.
While protoplasts consist of protoplasm and non-protoplasm. Protoplasm includes cytoplasm (cell fluid), cell nucleus (nucleus), and organelles.
Parts of protoplasts that belong to the non-protoplasmic category are vacuoles and ergastic substances. Such is the discussion of plant cell organelles, their functions and their components.



EmoticonEmoticon